Standards Alignment
Assessments, professional learning, family engagement, case studies.
NEW EUREKA MATH 2 ® PILOT PACKAGE
Are you looking for new ways to advance equity and build knowledge in your math classroom with high-quality instructional materials? EdReports recently reviewed Eureka Math 2 . Scan the QR code or access the final report .
Check out our special pilot package for only $10 per student.

Shop Online

SEE THE SCIENCE OF READING IN ACTION
At Great Minds ® , we’re committed to ensuring our curricula are aligned to the latest research on how students best learn to read, write, and build knowledge.
Explore webinars, blogs, research briefs, and more to discover how we incorporate this important body of research.

FREE CLASSROOM PRINTABLES
At Great Minds®, we’re committed to supporting educators with high-quality curricula and resources.
Explore resources designed to aid students in science and engineering and spark classroom conversation.
Webinar Library
Instructional resources, trending topics, knowledge-building, the science of reading, lesson design, universal design for learning (udl), background knowledge.
Palm Springs, CA
Houston, TX
New Orleans, LA
Eureka Math Student Materials: Grades K–5
Learn, Practice, Succeed
Learn, Practice, and Succeed from Eureka Math™ offer teachers multiple ways to differentiate instruction, provide extra practice, and assess student learning. These versatile companions to A Story of Units® (Grades K–5) guide teachers in response to intervention (RTI), provide extra practice, and inform instruction.
Also available for Grades 6–8 .
Learn, Practice, Succeed can be purchased all together or bundled in any configuration. Contact your account solutions manager for more information and pricing.

The Learn book serves as a student’s in-class companion where they show their thinking, share what they know, and watch their knowledge build every day!
Application Problems: Problem solving in a real-world context is a daily part of Eureka Math , building student confidence and perseverance as students apply their knowledge in new and varied ways.
Problem Sets : A carefully sequenced Problem Set provides an in-class opportunity for independent work, with multiple entry points for differentiation.
Exit Tickets: These exercises check student understanding, providing the teacher with immediate, valuable evidence of the efficacy of that day’s instruction and informing next steps.
Templates: Learn includes templates for the pictures, reusable models, and data sets that students need for Eureka Math activities.

With Practice , students build competence in newly acquired skills and reinforce previously learned skills in preparation for tomorrow’s lesson. Together, Learn and Practice provide all the print materials a student uses for their core instruction.
Eureka Math contains multiple daily opportunities to build fluency in mathematics . Each is designed with the same notion—growing every student’s ability to use mathematics with ease . Fluency experiences are generally fast-paced and energetic, celebrating improvement and focusing on recognizing patterns and connections within the material.
Eureka Math fluency activities provide differentiated practice through a variety of formats—some are conducted orally, some use manipulatives, others use a personal whiteboard, or a handout and paper-and-pencil format.
Sprints: Sprint fluency activities in Eureka Math Practice build speed and accuracy with already acquired skills. Used when students are nearing optimum proficiency, Sprints leverage tempo to build a low-stakes adrenaline boost that increases memory and recall. Their intentional design makes Sprints inherently differentiated – the problems build from simple to complex, with the first quadrant of problems being the simplest, and each subsequent quadrant adding complexity.

Eureka Math Succeed enables students to work individually toward mastery. Teachers and tutors can use Succeed books from prior grade levels as curriculum-consistent tools for filling gaps in foundational knowledge. Students will thrive and progress more quickly, as familiar models facilitate connections to their current, grade-level content.
Additional Problem Sets: Ideal for Homework or extra practice, these additional problem sets align lesson-by-lesson with what is happening in the classroom. These problems are sequenced from simple-to-complex to naturally scaffold student practice. They align with Eureka Math and use the curriculum’s mathematical models and language, ensuring that students feel the connections and relevance to their daily instruction, whether they are working on foundational skills or getting extra practice on the current topic.
Homework Helpers: Each problem set is accompanied by a Homework Helper, a set of worked examples that illustrate how similar problems are solved. The examples, viewed side by side with the homework, support students as they reinforce the day’s learning. Homework Helpers are also a great way to keep parents informed about math class.

Bundles and Class Sets Available
Bundle options are available for all of our materials (print, digital, PD, etc.). Prices vary by grade and size of class set. Certain grade-levels do not include all packets due to the nature of the grade-level content. Student workbooks are available in class sets of 20, 25, and 30. Prices vary by size of class set .

every child is capable of greatness
- Job Openings
- Digital Support
- Print Support
- Media Inquiries
Let’s Connect
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- System Status
- CA Residents: Do Not Sell My Info
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Place value
Unit 2: addition, subtraction, and estimation, unit 3: multiply by 1-digit numbers, unit 4: multiply by 2-digit numbers, unit 5: division, unit 6: factors, multiples and patterns, unit 7: equivalent fractions and comparing fractions, unit 8: add and subtract fractions, unit 9: multiply fractions, unit 10: understand decimals, unit 11: plane figures, unit 12: measuring angles, unit 13: area and perimeter, unit 14: units of measurement.
Curriculum / Math / 4th Grade / Unit 2: Multi-Digit Multiplication / Lesson 14
Multi-Digit Multiplication
Lesson 14 of 18
Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor tasks.
Problem Set
Target Task
Additional practice.
Multiply two-digit by two-digit numbers using four partial products.
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson
Number and Operations in Base Ten
4.NBT.B.5 — Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Foundational Standards
The foundational standards covered in this lesson
3.NBT.A.3 — Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10—90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
4.NBT.A.1 — Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division.
4.NBT.B.4 — Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.

Operations and Algebraic Thinking
3.OA.B.5 — Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Students need not use formal terms for these properties. Example: Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) Example: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.)
3.OA.C.7 — Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Understand that products can be computed by decomposing numbers into base-ten units, finding partial products of these base-ten units, then adding these partial products together based on the distributive property (e.g., $$36\times54=(30\times50)+(30\times4)+(6\times50)+(6\times4)$$ ). (Note that students need not know the term “distributive property.”)
- Multiply a two-digit whole number by a two-digit whole number using area models and the partial products algorithm.
- Estimate products by rounding factors to the largest place value.
- Solve one-step word problems involving multiplication of two-digit by two-digit numbers (on the Problem Set and Homework) (MP.4).
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
- Throughout the remainder of the topic, the main visual model used is the area model. If students seem to be struggling with place value understanding or don’t yet seem ready for the area model for some other reason, you might create a lesson to use before this one that focuses on the use of the base ten block array and/or graph paper array to build understanding toward the area model. The applet Partial Product Finder by The Math Learning Center may be helpful if you take that route. (See Unit-Specific Intellectual Prep section of the Unit Overview for examples of those representations.)
- Lessons 14 and 15 move through the various methods much more quickly than was done in Topic B, since they are already familiar with these methods and just extending them to two-digit by two-digit multiplication. If students struggled in Topic B, you might choose to use a flex day to solidify the strategies with two-, three-, and four-digit by one-digit multiplication or to extend Topic C over more days, having it more closely resemble Topic B.
- “When written methods are abbreviated, some students have trouble seeing how the single-digit factors are related to the two-digit numbers whose product is being computed (MP.2). They may find it helpful initially to write each two-digit number as the sum of its base-ten units (e.g., writing next to the calculation 94 = 90 + 4 and 36 = 30 + 6) so that they see what the single digits are. Some students also initially find it helpful to write what they are multiplying in front of the partial products (e.g., 6 × 4 = 24). These helping steps can be dropped when they are no longer needed” (NBT Progression, p. 15).
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Tasks designed to teach criteria for success of the lesson, and guidance to help draw out student understanding
Mr. Wynn now wants to cover a part of the gym with butcher paper to work on a large painting. He covers a section of the gym that is 30 feet long and 35 feet wide. Then he realizes he needs a bit more space for the painting and adds a section of butcher paper that is 4 feet long and 35 feet wide.
a. How many square feet of butcher paper did Mr. Wynn use for his painting?
b. What is the total length and width of Mr. Wynn’s painting?
Guiding Questions
Grade 4 Mathematics > Module 3 > Topic H > Lesson 36 of the New York State Common Core Mathematics Curriculum from EngageNY and Great Minds . © 2015 Great Minds. Licensed by EngageNY of the New York State Education Department under the CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 US license. Accessed Dec. 2, 2016, 5:15 p.m..
a. Label the area model to represent 31 × 23 and to find that product.
- Decompose each number into its base-ten units (tens and ones) and write them in the boxes on each side of the rectangle.

- Label regions A, B, C, and D with their areas. Show your reasoning.
- Find the product that the area model represents. Show your reasoning.
b. Here is one way to calculate 31 × 23. Each number with a box gives the area of one region in the area model.

- In the boxes next to each number, write the letter of the corresponding region.
- There is a 1 above the hundreds digit in the sum. What does that 1 represent?
Grade 6 Unit 5 Lesson 7 (Teacher Version) is made available by Open Up Resources under the CC BY 4.0 license. Copyright © 2017 Open Up Resources. Download for free at openupresources.org. Accessed Dec. 14, 2018, 4:05 p.m..
Estimate each product. Then use any method to solve.
a. $$26\times37$$
b. $$81\times52$$
c. $$68\times73$$
Unlock the answer keys for this lesson's problem set and extra practice problems to save time and support student learning.
Discussion of Problem Set
- Why is it possible to represent #8 with an area model even though it is not an area problem?
- When working with a two-digit by two-digit multiplication problem, how many partial products are there usually? What if one of the two-digit numbers has a 0 in the ones place? What if they both do?
- How did our previous work with area models and partial products help us to be ready to solve two-digit by two-digit multiplication problems using four partial products?
- How could you explain to someone that ones x tens equals tens but tens x tens equals hundreds ?
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
Zora solves 12 × 64 using an area model.

Use the same reasoning as Zora to solve 35 × 19. Find each partial product in the area model and then fill in the blanks to complete the equation.

Student Response
An example response to the Target Task at the level of detail expected of the students.
The Extra Practice Problems can be used as additional practice for homework, during an intervention block, etc. Daily Word Problems and Fluency Activities are aligned to the content of the unit but not necessarily to the lesson objective, therefore feel free to use them anytime during your school day.
Extra Practice Problems
Answer keys for Problem Sets and Extra Practice Problems are available with a Fishtank Plus subscription.
Word Problems and Fluency Activities
Help students strengthen their application and fluency skills with daily word problem practice and content-aligned fluency activities.
Topic A: Multiplicative Comparison
Solve multiplicative comparison problems with a larger unknown. Distinguish multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.
4.OA.A.1 4.OA.A.2
Solve multiplicative comparison problems with a smaller unknown.
Solve multiplicative comparison problems with an unknown multiplier. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison.
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Multiplication of up to Four-Digit Whole Numbers by One-Digit Whole Numbers
Multiply 10, 100, and 1,000 by one- and two-digit numbers.
Multiply multiples of 10, 100, and 1,000 by one-digit numbers. Estimate multi-digit products by rounding numbers to their largest place value.
Multiply two-, three-, and four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers using a variety of mental strategies.
Multiply two-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
Multiply three-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
Multiply four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
Multiply two-, three-, and four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers and assess the reasonableness of the product.
Topic C: Multiplication of Two-Digit Whole Numbers by Two-Digit Whole Numbers
Multiply two-digit multiples of 10 by two-digit multiples of 10. Estimate multi-digit products by rounding numbers to their largest place value.
Multiply two-digit multiples of 10 by two-digit numbers.
Multiply two-digit numbers by two-digit numbers using a variety of mental strategies.
Multiply two-digit by two-digit numbers using two partial products and assess the reasonableness of the product.
Topic D: Multi-Step Word Problems
Abstract the formulas for the area and perimeter of a rectangle and apply those formulas in real-world and mathematical problems involving multiplication, addition, and subtraction.
4.MD.A.3 4.OA.A.3
Solve two-step word problems involving multiplication, addition, and subtraction.
4.OA.A.2 4.OA.A.3
Solve multi-step word problems involving multiplication, addition, and subtraction.
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.
Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

Effective Instruction Made Easy
Access rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 14 Answer Key
Anyone who wishes to prepare Grade concepts can get a strong foundation by accessing the Eureka Math Book Answer Key. People of highly subject expertise prepared the solutions in a concise manner for easy grasping. Start answering all the questions given in Eureka Math Book Grade 2 Answer Key. Refer to our Eureka Math Answers Grade 2 chapter 14to enhance your math skills and also to score good marks in the exams.
Engage NY Eureka Math 2nd Grade Module 4 Lesson 14 Answer Key
Eureka’s Math Answer Key for Grade 2 meets the content and intent of the school curriculum. By using the Eureka Math Grade 2 Answer Key, you can understand the topics of all chapters easily. Detailed solutions provided make it easy for you to grab Knowledge and learn the underlying concepts. Download Eureka Math Answers Grade 2 pdf for free. Tp the links and practise well for the exams
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 14 Problem Set Answer Key
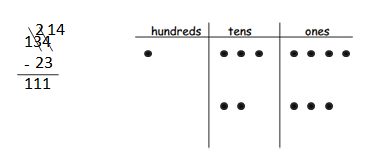
Answer: 134 – 23 = 111.
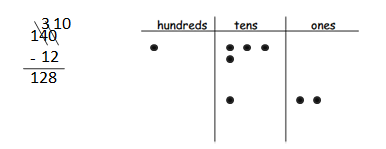
Answer: 140 – 12 = 128.
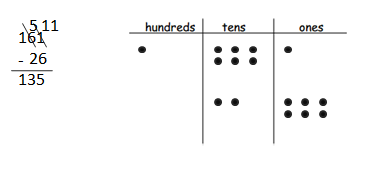
Answer: 161 – 26 = 135.
Answer: 187 – 49 = 138.
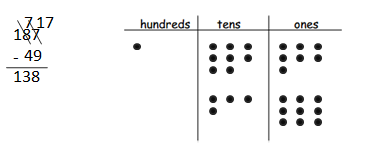
Question 2. Solve the following problems vertically without a place value chart. a. 63 – 28 = __35____
Answer: 63 – 28 = 35.
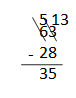
b. 163 – 28 = ___135____
Answer: 163 – 28 = 135.
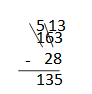
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 14 Exit Ticket Answer Key
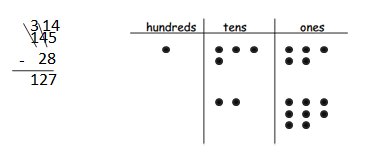
Solve by writing the problem vertically. Check your result by drawing chips on the place value chart. Change 1 ten for 10 ones, when needed.
Answer: 145 – 28 = 127.
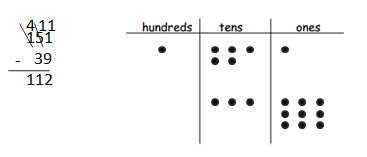
Answer: 151 – 39 = 112.
Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key
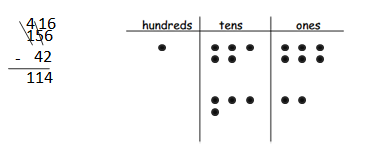
Answer: 156 – 42 = 114.
Answer: 150 – 36 = 114.
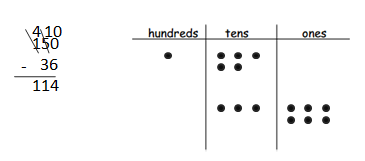
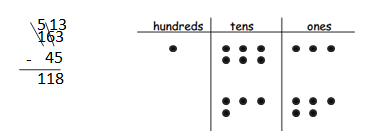
Answer: 163 – 45 = 118.
Answer: 134 – 29 = 105.
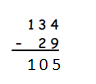
Answer: 154 – 37 = 117.
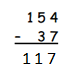
Question 3. Solve and show your work. Draw a place value chart and chips, if needed. a. Aniyah has 165 seashells. She has 28 more than Ralph. How many seashells does Ralph have?
Answer: The number of seashells does Ralph have = 137.
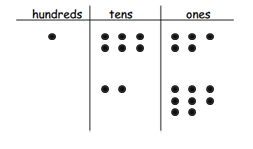
b. Aniyah and Ralph each give 19 seashells to Harold. How many seashells does Aniyah have left?
Answer: The number of seashells do Aniyah have left = 146.
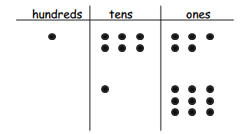
c. How many seashells does Ralph have left?
Answer: The number of seashells does Ralph have left = 118.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, Aniyah and Ralph each give 19 seashells to Harold. 137 – 19 = 118. so the number of seashells do Ralph have left = 118.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 4 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. Draw triangles that fit the following classifications. Use a ruler and protractor. Label the side lengths and angles. a. Right and isosceles Answer: b. Right and scalene Answer: c. Obtuse and isosceles Answer: d. Acute and scalene Answer: Question 2.
It's Homework Time! Help for fourth graders with Eureka Math Module 4 Lesson 14.
Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 1 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. Use the standard algorithm to solve the following subtraction problems. a. Answer: Explanation: In subtraction if the minuend place values are less than the subtrahend then 1 is borrowed from the higher place value like.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 3 Lesson 14For more Eureka Math (EngageNY) videos and other resources, please visit http://EMBARC.onlinePLEASE leave a me...
4/3 > 7/6. Eureka Math Grade 4 Module 5 Lesson 14 Homework Answer Key. Question 1. Compare the pairs of fractions by reasoning about the size of the units. Use >, <, or =. a. 1 third _____ 1 sixth. Answer: 1 third > 1 sixth. Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, compare the pairs of fractions by reasoning about the size of the ...
Grade 4 Module 6 Collapse all Expand all. Decimal Fractions. Eureka Essentials: Grade ... Homework Solutions File. Promethean Flipchart Page. Google Slides Page. ... Lesson 14 Video Page. Lesson PDF Page. Homework Solutions File. Promethean Flipchart Page. Google ...
Lesson 14: Find common units or number of units to compare two fractions. Lesson 14 Homework 4• 5 Name Date 1. Compare the pairs of fractions by reasoning about the size of the units. Use >, <, or =.
The source for the homework pages is the full module PDF, available for free here:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-3-mathematics-module-4
With Practice, students build competence in newly acquired skills and reinforce previously learned skills in preparation for tomorrow's lesson. Together, Learn and Practice provide all the print materials a student uses for their core instruction. Eureka Math contains multiple daily opportunities to build fluency in mathematics.Each is designed with the same notion—growing every student ...
4th grade 14 units · 154 skills. Unit 1 Place value. Unit 2 Addition, subtraction, and estimation. Unit 3 Multiply by 1-digit numbers. Unit 4 Multiply by 2-digit numbers. Unit 5 Division. Unit 6 Factors, multiples and patterns. Unit 7 Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions. Unit 8 Add and subtract fractions.
3.NBT.A.3 — Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10—90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations. 4.NBT.A.1 — Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right.
NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 4•4 Lesson 14: Define and construct triangles from given criteria. Explore symmetry in triangles. Date: 10/16/13 4.D.44 ... NYS COMMON CORE MATHEMATICS CURRICULUM 14 Homework 4•Lesson 4 Lesson 14: Define and construct triangles from given criteria. Explore symmetry in triangles. Date: 10/16/13 4.D.45
Eureka Essentials: Grade 4. An outline of learning goals, key ideas, pacing suggestions, and more! Fluency Games. Teach Eureka Lesson Breakdown. Downloadable Resources. Teacher editions, student materials, application problems, sprints, etc. Application Problems. Files for printing or for projecting on the screen.
The source for the homework pages is the full module PDF at this address:https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-2-mathematics-module-4
Answer: 4 bows can be made from 3 feet of ribbon, Left over ribbon will be 4 inches, Explanation. Given If it takes 8 inches of ribbon to make a bow, So how many bows can be made from 3 feet of ribbon. (1 foot = 12 inches) are 3 X 12 = 36 inches ÷ 8 inches =. 4 quotient (8 X 4 = 32) and 4 inches remainder means|.
Grade 4 Module 4. Topic A: Lines and Angles. Lesson 1. Lesson 2. Lesson 3. Lesson 4. Topic B: Angle Measurement. Lesson 5. Lesson 6. Lesson 7. Lesson 8. Mid-Module Review. Topic C: Problem Solving with the Addition of Angl... Lesson 9. Lesson 10. Lesson 11. Topic D: Two-Dimensional Figures and Symmetry. Lesson 12. Lesson 13. Lesson 14. Lesson ...
Multiply unit fractions by non unit fractions, common core, area models, tape diagrams, word problems, cross cancel, simplify, help students, help teachers, ...
Displaying all worksheets related to - Grade 4 Lesson 14 Homework. Worksheets are Homework and remembering, 001 001 cr14 na gp 4 u1w1d1 114244, Eureka math homework helper 20152016 grade 4 module 1, English work, Spelling grade 4 spelling, Grade 4, Grade 4, Latin and greek word roots grade 4. *Click on Open button to open and print to worksheet. 1.
EngageNY/Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Lesson 14For more videos, please visit http://bit.ly/engageportalThis is a looooong video. Consider breaking it up and ...
Eureka Math Grade 5 Module 4 Lesson 14 Exit Ticket Answer Key. Question 1. Solve. Draw a rectangular fraction model to explain your thinking. Then, write a number sentence. of =. Question 2. In a cookie jar, of the cookies are chocolate chip, and of the rest are peanut butter.
Here is a Link to the source pages: https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-1-mathematics-module-4I used the "full module" PDF.
Tila cuts a 3 cm by 4 cm rectangle out of hers, Evan cuts 2 cm by 6 cm rectangle out of his. 3 x 5 = 15. 4 x 3 = 12. so Tila is correct. Eureka Math Grade 3 Module 4 Lesson 14 Exit Ticket Answer Key. Mary draws an 8 cm by 6 cm rectangle on her grid paper. She shades a square with a side length of 4 cm inside her rectangle.
2 x 10 = 20. 8 x 1 = 8. 100 + 60 + 3 = 163. 20 + 8 = 28. 163 - 28 = 135. Eureka Math Grade 2 Module 4 Lesson 14 Exit Ticket Answer Key. Solve by writing the problem vertically. Check your result by drawing chips on the place value chart. Change 1 ten for 10 ones, when needed.